Gustave Roussy Cancer Center
企業/大学
Gustave Roussy Cancer Center
チームメンバー
リサーチ・ディレクター:グイド・クローマー
チームリーダー:オリバー・ケップ
教員メンバー:アラン・ソーヴァ、マリオン・ルドゥック
使用製品
ImageXpress Micro XLS ハイコンテントイメージングシステム
課題
クローマー研究室は、細胞ストレスと細胞死の分子メカニズムに興味を持っている。がん治療中に誘発される細胞ストレスと細胞死の様式は、治療に重大な影響を及ぼす。どの特定の細胞ストレスや細胞死サブルーチンが優先的に実行されるかを "決定 "する分子スイッチを同定するために、系統的な探索が開始された。さらに、がん細胞死の様式とそれらが免疫系に与える影響を系統的に分析し、治療成功の可能性を高める戦略を開発している。
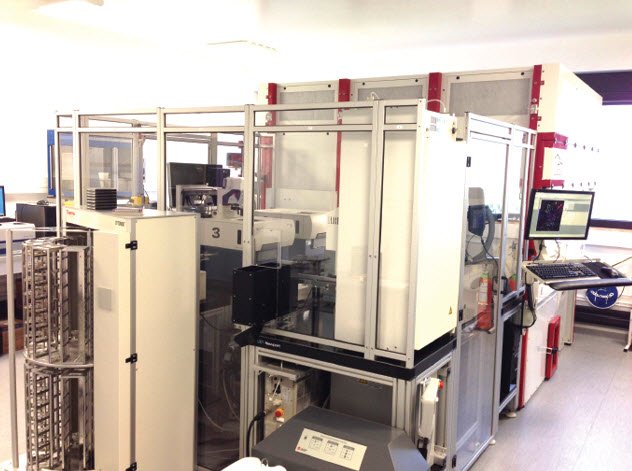
クローマー研究所のセルバイオロジープラットフォーム(写真右)は、大規模化合物やsiRNAライブラリーの表現型スクリーニングを可能にする完全自動化された細胞生物学ワークフローを提供するため、スクリーニングアプローチを実施するハブとして使用されている。この研究室では、あらゆる種類の細胞ストレスと細胞死を評価するために、蛍光バイオセンサー・バッテリーを使用している。
この最先端の研究を可能にするために、同グループは、化合物管理と自動細胞培養も含む自動化プラットフォームに完全統合できるハイコンテント分析システムを必要としていた。

解決策
同グループは、ImageXpress® Micro XLS ハイコンテントイメージングシステムに決定する前に、慎重に市場をスクリーニングし、利用可能なシステムのほとんどをテストした。現在、グループ内には5台のImageXpressシステムがあり、そのうち2台は自動化プラットフォームに常設されており、1台は必要に応じてプラットフォームに出し入れできるようになっている。
彼らが決定した構成では、強力なLEDライトエンジンと組み合わせてマルチバンドパスフィルターを使用することができ、機械的な動きを最小限に抑えることができるため、取得が極めて高速になる。
ImageXpressシステムを統合することで、プラットフォーム上で2台の同一構造のマシンが並行して動作することによるスピードと、冗長性による信頼性を提供するソリューションを構築することができました」とケップは語った。
データ取得と解析には、MetaXpress®ハイコンテント画像取得・解析ソフトウェアとカスタムメイドのRアルゴリズムを使用している。
使用製品
-
ImageXpress Micro XLS ハイコンテントイメージングシステム
ImageXpress Micro XLSハイコンテントイメージングシステムは、最新のImageXpress HCS.aiハイコンテントスクリーニングシステムに置き換わっています。この最新システムはユーザーが必要とする要件に合わせて構成可能で、研究のニーズの進化に合わせてアップグレードすることができます。
結果
同グループのプラットフォームのユニークなデザインは、自動化された細胞培養と化合物管理と、産業用ロボットを介した3つの完全自動ハイコンテント分析システムを統合しているため、非常に柔軟なアッセイデザインとマルチプレックスを可能にしている。
「ImageXpressシステムとMetaXpress®ソフトウェアは信頼性が高く、使いやすい。MetaXpressが情報を保存しているSQLデータベースを使用して、必要なデータマイニングツールをすべてRでコーディングしました。このアプローチにより、最小限の時間で画像から棒グラフに変換することができます。
全ゲノムスクリーニングのスループットは67 x 384プレートであり、このプラットフォームは1週間で全ゲノムスクリーニングを行う。siRNAスクリーニングを除けば、自動化は主に異なる次元(濃度、時間、組み合わせ)の化合物ライブラリーのスクリーニングに使用される。
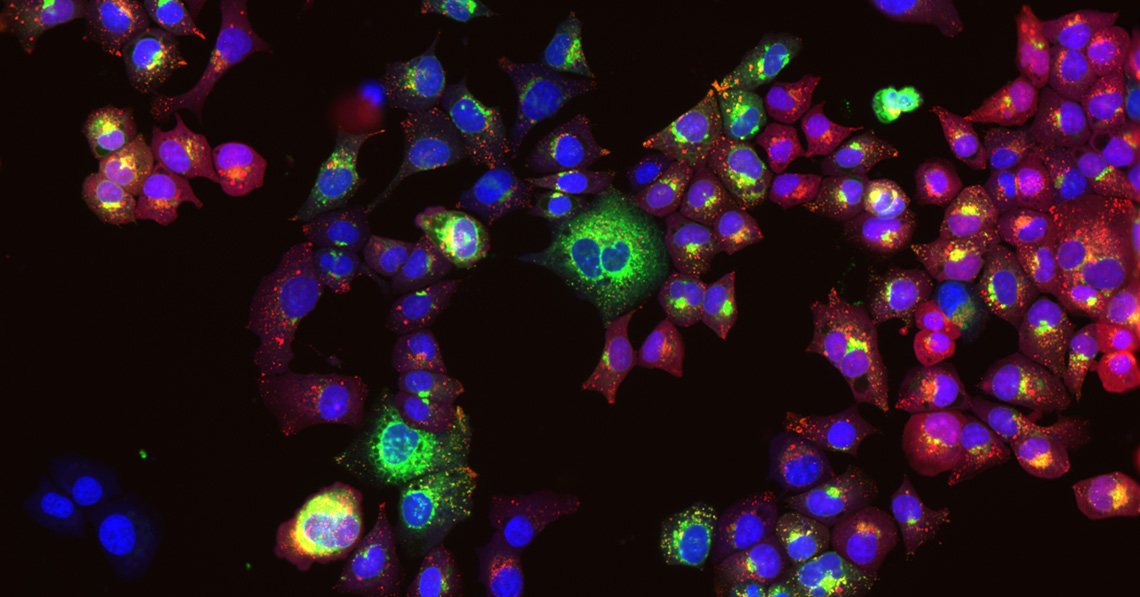
この技術が可能にする研究の一例として、研究グループは最近、トランス脂肪酸が飽和脂肪酸によって誘導されるオートファジーを阻害することを示すことができた(画像)。
"ImageXpressシステムとMetaXpress®ソフトウェアは信頼性が高く、使いやすい。"
オリバー・ケップ
参考文献
1) Sauvat A., et al. (2018). Trans-Fats Inhibit Autophagy Induced by Saturated Fatty Acids. EBioMedicine. pii: S2352-3964 (18) 30115-4. [Epub ahead of print].
2) Bezu L., et al. (2018). eIF2α phosphorylation is pathognomonic for immunogenic cell death. Cell Death & Differentiation. [Epub ahead of print].
3) Liu P., et al. (2017). Identification of pharmacological agents that induce HMGB1 release. Scientific Reports, 7 (1): 14915.
4) Sauvat A., et al. (2017). Automated Analysis of Fluorescence Colocalization: Application to Mitophagy. Methods in Enzymology, 588: 219-230.
5) Zhou H., et al. (2016). The oncolytic compound LTX-401 targets the Golgi apparatus. Cell Death & Differentiation, 23 (12): 2031-2041.


